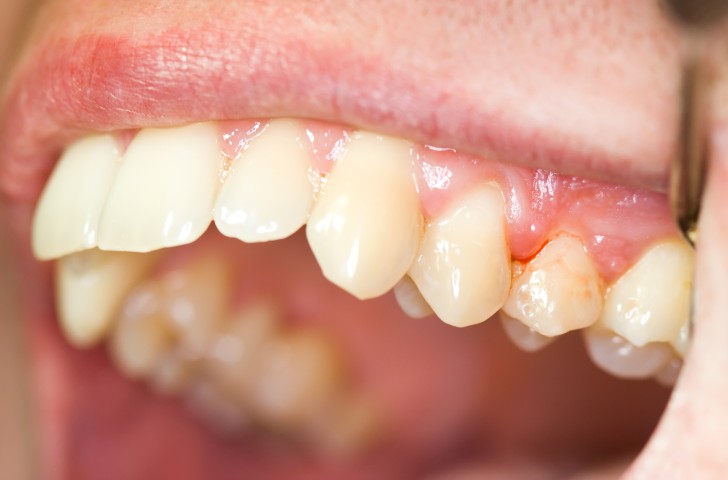
Bleeding gums typically tend to indicate some degree of periodontal disease, which is marked by inflammation in the gum tissue. Gum disease is a progressive condition that tends to respond well when treated in its mildest forms. However, as the condition advances, the interventions needed to address the problem become more invasive. Eventually, gum surgery may be needed to reverse the damage.
Similarly, the harm that can occur from untreated advanced gum disease becomes more significant. For example, patients with severe periodontitis may be at risk for tooth or bone loss. As a result, the patient may develop a need for a tooth replacement such as a dental implant.
When tooth loss occurs as a result of gum disease, your nutrition may suffer along with your smile’s appearance. Most tooth replacement devices do not have a root-like structure underneath the gum line so they aren’t as good at chewing. The one exception is the dental implant, with which the jawbone is able to bond. Therefore, dental implants offer the most structurally complete tooth replacement available.
Gum disease has wide-reaching effects beyond your smile’s appearance and even your oral health. This condition appears to have a correlation with other systemic problems like heart disease and diabetes. While the mechanism for this link is not fully understood, it may be related to the inflammation found in all of these diseases.
Bleeding gums should never be ignored. If you develop this symptom, consult with your dental provider for further attention and to plan for the best course of action to treat your gum disease. The effects of gum disease can have an impact beyond your smile, so your mouth and body will benefit from quick attention to periodontal disease.
If you’ve been referred to us, or simply have questions about our treatment, contact our office today!